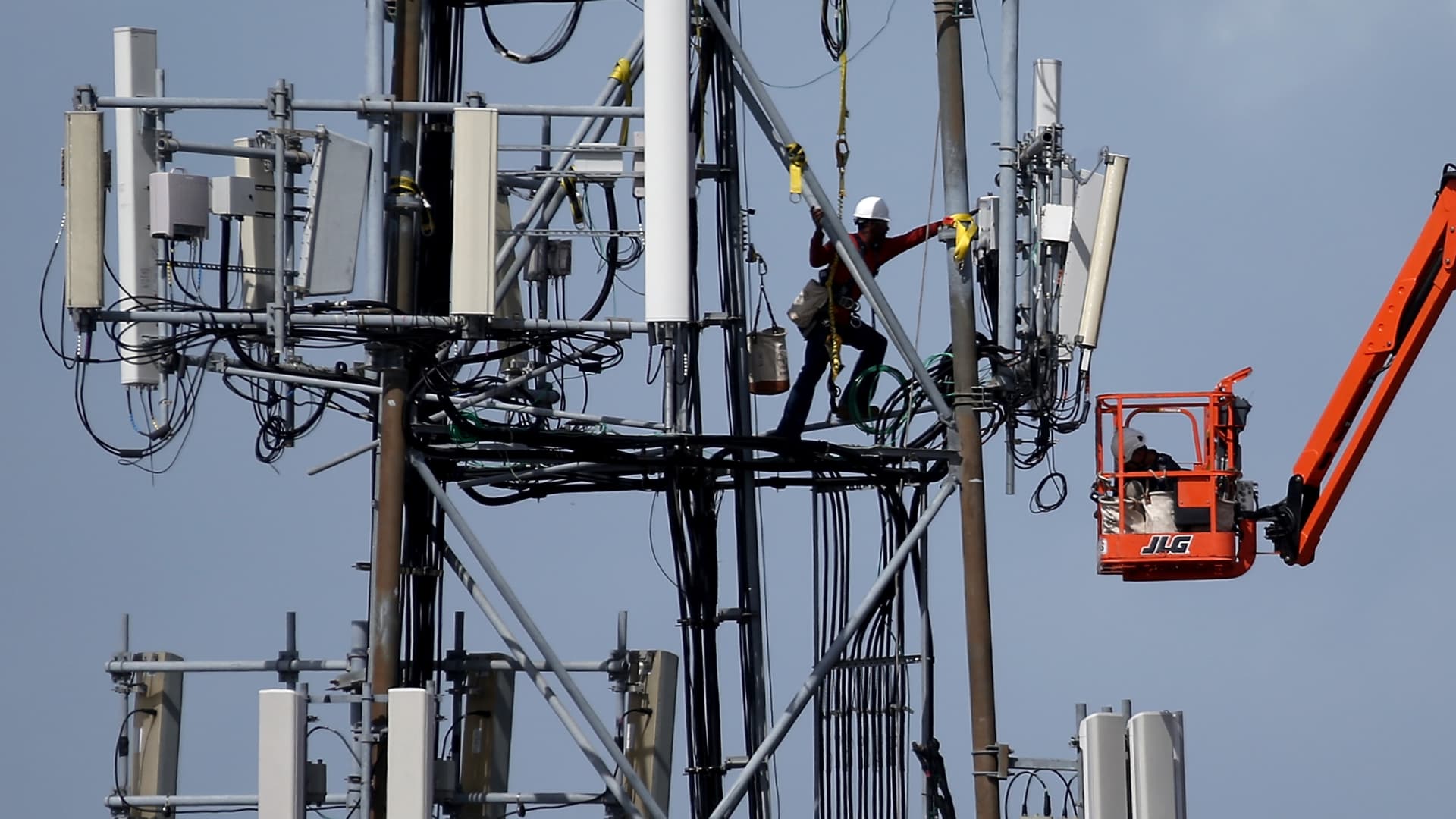
C.E.O. of Tesla, Chief Engineer of SpaceX and C.T.O. of X Elon Musk takes the stage during the New York Times annual DealBook summit on November 29, 2023 in New York City.
Michael M. Santiago | Getty Images
Tesla CEO Elon Musk is asking the U.S. Supreme Court to undo a settlement agreement that he and the automaker struck with the Securities and Exchange Commission requiring a company lawyer, or a “Twitter sitter,” to review and approve his Tesla-related tweets.
In a petition on Dec. 7, Musk’s attorneys alleged that the “Twitter sitter” provision in the agreement violated their client’s free speech rights. They argue Musk was coerced into agreeing with “unconstitutional conditions.”
The SEC charged Musk with civil securities fraud after he posted a series of tweets in 2018 saying he had “funding secured” to take Tesla private for $420 per share, and that “investor support” for such a deal was “confirmed.” Trading in Tesla was halted after his tweets, and shares remained volatile in the weeks that followed.
Musk and Tesla settled with the regulator and then revised the agreement in April 2019. Since then, the SEC has continued to investigate Musk and Tesla to ensure that they’re complying with the terms.
The settlement “restricts Mr. Musk’s speech even when truthful and accurate,” his lawyers wrote. “It extends to speech not covered by the securities laws and with no relation to the conduct underlying the SEC’s civil action against Mr. Musk. And it chills Mr. Musk’s speech through the never-ending threat of contempt, fines, or even imprisonment for otherwise protected speech if not pre-approved to the SEC’s or a court’s satisfaction.”
Musk purchased Twitter in 2022 and renamed it X this year. He is the company’s chairman and chief technology officer.
Columbia Law School professor Eric Talley, who specializes in corporate and business law, described the effort as a “swing for the fences” move in an email to CNBC. A circuit court has already refused to hear the appeal. To win a hearing from the Supreme Court, Musk would need four of the nine justices to agree to take the case.
Talley said the “unconstitutional conditions” doctrine that’s at the heart of Musk’s argument is usually “in play when the government is doling out various types of general public benefits,” such as getting a tax break for promising not to criticize the Supreme Court.
“It’s at core a very slippery doctrine,” Talley said. “But this case is more like the government agreeing to forebear from pursuing charges against someone in exchange for their agreement to cooperate with the terms of the settlement. That’s not general doling out of benefits.”
Talley added that for a person of means like Musk, it may be worth “spinning the judicial roulette wheel.”
The SEC didn’t immediately respond to a request for comment.
Separately, Tesla investors have sued the company and Musk over the “funding secured” tweets and their impact to the stock price. In February, a jury in a San Francisco federal court found Musk and Tesla were not liable in a class action securities fraud trial. The shareholders have filed for an appeal to the 9th Circuit.
Read the petition to SCOTUS here: